Blog
How to Use the New Redis Data Source for Grafana Plug-in
Earlier this month, Redis released the new Redis Data Source for Grafana plug-in, which connects the widely used open source application monitoring tool to Redis. To give you an idea of how it all works, let’s take a look at a self-referential example: using the plug-in to see how many times it has been downloaded over time. (The Grafana plug-in repository itself does not provide such statistics out of the box.)
Want to learn more? Read Introducing the Redis Data Source Plug-in for Grafana
What is the Redis Data Source for Grafana?
If you’re not familiar with Grafana, it’s a very popular tool used to build dashboards to monitor applications, infrastructures, and software components. The Redis Data Source for Grafana is a plug-in that allows users to connect to the Redis database and build dashboards in Grafana to easily monitor Redis data. It provides an out-of-the-box predefined dashboard, but also lets you build customized dashboards tuned to your specific needs.
The Redis Data Source for Grafana plug-in can be installed using grafana-cli, Docker, or used in the Grafana Cloud. Alternatively the plug-in can be built from scratch following the instructions on GitHub.
grafana-cli plugins install redis-datasource
Prerequisites
This demo uses:
- Node.js 10.x with Node package manager (npm)
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- Redis 5.0.x or later with RedisTimeSeries (this demo uses the Redis Docker container)
- Grafana 7.0 or later with Redis Data Source (this demo uses the Grafana Docker container)
How to retrieve Grafana plug-in information
Information about any registered plug-in in a Grafana repository can be retrieved using the API in JSON format:
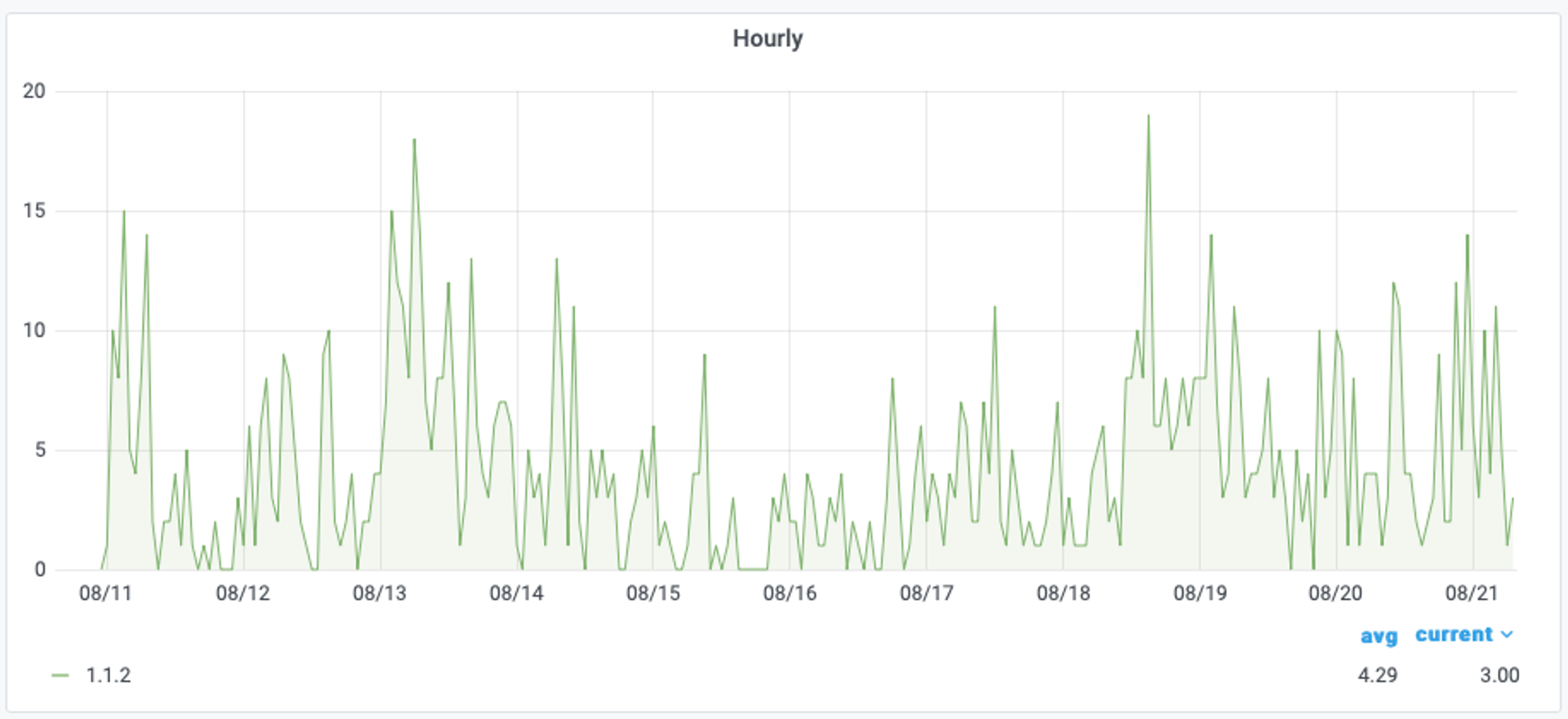
For this example, I wanted to find out how many times Redis Data Source for Grafana plug-in was downloaded per day, and to look for spikes after we tweeted or posted on the Redis blog about it. I decided to use RedisTimeSeries (a Redis module that adds a time-series data structure to Redis) to track the number of downloads every hour.
To populate the data I used the TS.ADD command with an automatic timestamp and labels `plugin` and `version`. X is a number of downloads and the latest version `1.1.2` retrieved from API. Labels will be used later to query the time series.
I wrote a simple script using ioredis and Axios libraries to call the API and use plug-in information to add time-series samples:
My script environment
I used a package.json file to install dependencies and ran commands using `npm` as shown here:
To orchestrate Docker containers, I used docker-compose:
- The Redis service is based on a redis/redistimeseries image, which has the RedisTimeSeries module enabled.
- The Grafana service uses the latest Grafana release with the Redis Data Source plug-in installed from the repository.
To run the script every hour and collect the download data, I used crontab on the Linux server in the cloud:
Testing the Redis Data Source for Grafana plug-in
To run the script and collect data, you need to install Node.js, Docker, and Docker Compose, following the instructions for your operating system:
After running the script, we can check the RedisTimeSeries data using the TS.MRANGE command. You can query a range across multiple time-series by using filters in forward or reverse directions:
The command TS.MRANGE with filter `plugin` retrieves samples only for the `redis-datasource` plug-in. Use the option WITHLABELS to return labels.
How to display RedisTimeSeries data in Grafana
Open Grafana in a web browser using `http://localhost:3000` and create the data source by selecting Configuration -> Data Sources. Redis Data Source for Grafana supports transport layer security (TLS) and can connect to open source Redis OSS, Redis Enterprise, and Redis Enterprise Cloud databases anywhere using a direct connection.
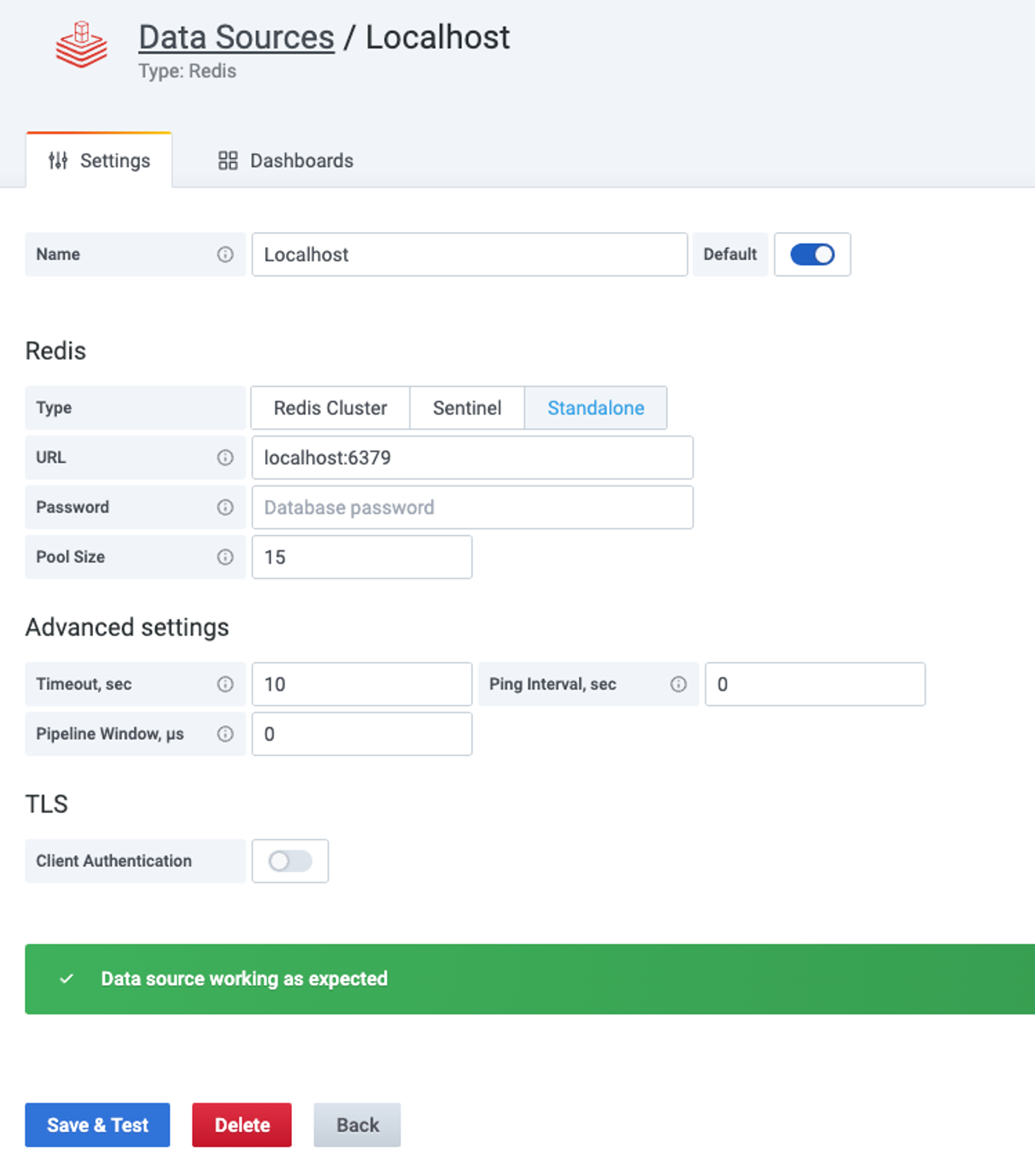
Adding Redis Data Source to Grafana configuration information.
The next step is to create a dashboard with a graph panel to visualize data. Select “Redis Datasource” and “RedisTimeSeries commands” in the query editor. Use the command TS.MRANGE with a plug-in name filter.
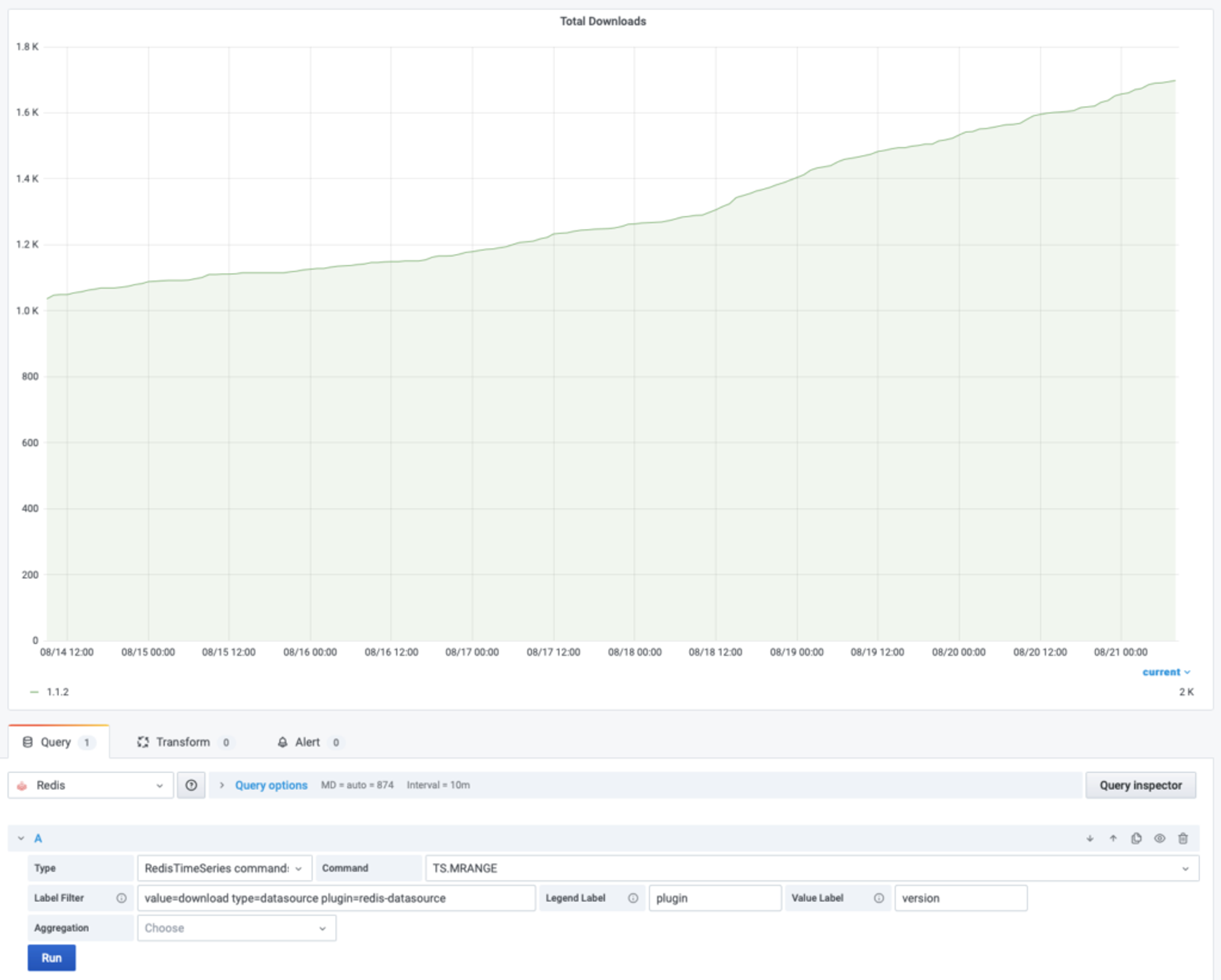
Finally, I named the plug-in Legend Labels and set the version as Value Label, which will make it easier to display the series for later versions of Redis Data Source for Grafana.
Checking the results
Use the command TS.INFO to see the information and statistics for the time series. So far I have collected download data for 250 hours and can see how much memory (in bytes) was allocated to store time-series and other information.
At the time of publication, Redis Data Source for Grafana plug-in has been downloaded more than 3500 times! We have received valuable feedback from the community and continue developing new features for the data source.
For more information, look at the GitHub repository for the project and let us know if you have any questions in the issues.
Conclusion
I hope this post, and my example using the Redis Data Source for Grafana to track downloads of the plug-in over time, has demonstrated the power and ease of use of this new tool and inspires your to monitor your application data (transactions, streams, queues, etc.) using RedisTimeSeries. Stay tuned for more posts on how and why to use the Redis Data Source for Grafana plug-in.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.
